ROCKEFELLER UNIVERSITY PRESS - Researchers from St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have discovered that inhibiting an enzyme called cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) protects mice and rats from noise- or drug-induced hearing loss. The study, which will be published March 7 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, suggests that CDK2 inhibitors prevent the death of inner ear cells, which has the potential to save the hearing of millions of people around the world.
According to the World Health Organization, 360 million people worldwide, including 32 million children, suffer from hearing loss caused by congenital defects or other factors. These factors include infectious disease, use of certain medicines, or exposure to excessive noise. Yet, there are currently no FDA-approved drugs to prevent or treat hearing loss.
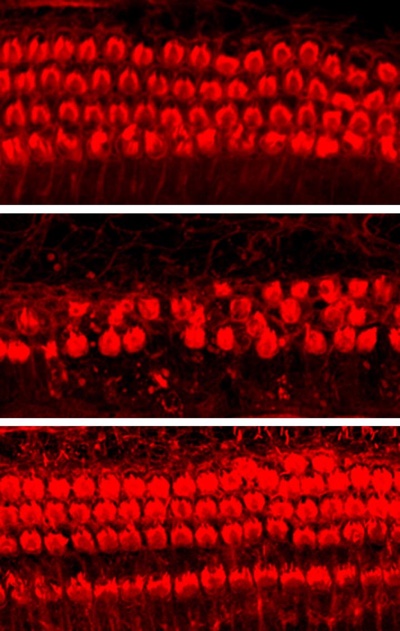
Compared with a normal mouse cochlea (top), cisplatin exposure reduces the number of outer hair cells (middle). But the loss of these cells is prevented by treatment with the CDK2 inhibitor kenpaullone (bottom). Photo courtesy of Teitz et al., 2018.
A team of researchers led by Dr. Jian Zuo screened over 4,000 drugs for their ability to protect cochlear cells from the chemotherapy agent cisplatin. Cisplatin is used to treat a variety of cancers but causes irreversible hearing loss in up to 70% of patients.
Zuo and colleagues identified multiple compounds that protected cochlear cells from cisplatin, several of which are already approved to treat other conditions. Three of the ten most effective compounds were inhibitors of an enzyme called CDK2. One of these CDK2 inhibitors, kenpaullone, was more effective than four other compounds that are currently in clinical trials for treating hearing loss.
Injecting kenpaullone into the middle ear protected both mice and rats from cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Moreover, kenpaullone also protected the hearing of mice to noise as loud as 100 dB. "Given that 100-dB noise is in the range of noise insults commonly experienced by people in our society, kenpaullone could have significant clinical application in treating noise-induced hearing loss," says Zuo.
In the case of cisplatin-induced hearing loss, kenpaullone appears to protect hair cells by preventing CDK2 from stimulating the production of toxic reactive oxygen species from the cells' mitochondria.
"The robust protection conferred by one-time local delivery of kenpaullone suggests that CDK2 inhibitors may transform the clinical prevention and treatment of cisplatin- and noise-induced hearing loss in patients," Zuo says. "Modifications of the treatment regimens, additional optimization of the delivery methods via the use of hydrogels, and structural modifications of the compounds via medicinal chemistry could ensure even better results with CDK2 inhibitors in treating hearing loss in humans."
###
Teitz et al., 2018. J. Exp. Med. https://jem.
About the Journal of Experimental Medicine The Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) features peer-reviewed research on immunology, cancer biology, stem cell biology, microbial pathogenesis, vascular biology, and neurobiology. All editorial decisions are made by research-active scientists in conjunction with in-house scientific editors. JEM provides free online access to many article types from the date of publication and to all archival content. Established in 1896, JEM is published by Rockefeller University Press. For more information, visit jem.org.
Source: https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2018-03/rup-rin022818.php

